|
The baleen consists of triangular horned plates built of keratin, the same material as in nails. These plates are densely packed inside the mouth and are used for filtrating plankton from the sea water. Depending on species, between 200 and 400 baleen plates hang down from each side of the upper jaws.
Of the 83 whale species, only 11 are baleen whales. In the Greenland right whale, the baleen can reach a length of 4 metres, but in most species these structures are considerably shorter.
In its natural state, the baleen is almost soft, and attached to a very elastic “gum ”. On the inside they look fluffy. As the baleen stands very dense inside the mouth, it almost forms a carpet-like structure which makes the whales better able to filter the sea water.
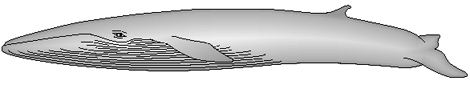
Fin whales trap their food by gulping large amounts of sea water containing plankton.
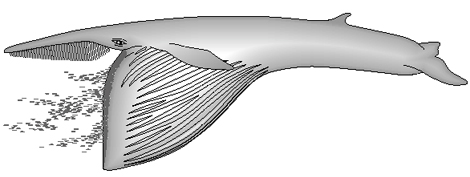
By a special jaw joint they are able to open their mouth so wide that the lower jaw stands almost 90 degrees on the upper jaw. Sea water is pushed under the tongue so that this is converted into a sac-like structure that is forced into the throat region and forms a cavity (cavum ventrale).
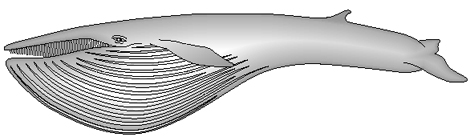
The mouth is almost closed, and the effect of the water pressure almost disappears. All the stretched tissue of the throat region regains its original shape, and the water is pushed towards the front of the mouth where the plankton and other food are filtrated by the baleen. When all the water is pushed out, the tongue regains its shape and is used for cleansing plankton off the baleen so that it can be swallowed.
The right whales use another technique. They lack baleen in the front of their mouth where it is an opening. When they swim through plankton-rich water with their mouth open, the water is pressed out and filtrated through the baleen of the sides of the mouth. This filter could then be cleaned by the tongue, and the plankton is swallowed.
Toothed whales find their food by eco-location. In this process, the animals emit high-frequent sound from the nasal cavity through a large, lens-shaped wax structure in the forehead (the melon). Sound is reflected by the prey and is detected by the whales’ inner ears via oil-filled canals in the lower jaws.
|



